To put it simply, a booster should help a plant take up nutrients. The uptake of nutrients depends on the plant's health and metabolic rate. The problem is that most 'boosters' are just additional nutrients. True boosters like CANNABOOST, however, really boost the metabolism of a plant and make it more healthy. But it's not easy to manufacture CANNABOOST. In this article we explain what it takes to make CANNABOOST and how it works in a plant.
What are nutrients?

In order to understand how CANNABOOST works, we first have to understand what nutrients are. Most people know that plants need nutrients to grow, even if they may not know exactly what plant nutrients really are, or what they consist of.
Plants take up nutrients from the medium they are growing in through their roots system. The growing medium may be of natural origin, such as peat or coco, or it may be artificial, such as rock wool or clay pebbles.
Some plant species, like many orchids and other epiphytes (plants that grow non-parasitically on other plants) take up nutrients through their leaves. They use their roots system mainly for holding onto the branches or other structures on which they are growing.
Macro elements and trace elements
Nutrients can be divided into macro elements and micro (trace) elements. Macro elements include:
These elements are taken up by plants in relatively large quantities. The first three are known as primary nutrients: N, P, and K. The next three are secondary elements: Ca, Mg, and S. Minor or trace elements are needed in smaller quantities and they include:
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Iron (Fe)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Copper (Cu)
- Molybdenum (Mo)
- Boron (B)
- Manganese (Mn)
Although they are only needed in tiny amounts, this last group of nutrients is still vital for a plant’s metabolism and health. Carbon (C), Oxygen (O) and Hydrogen (H) are not listed here, but they are nutrients as well. These are obtained from the plant’s environment.

Even if all the necessary nutrients are available in the optimum quantities, the actual uptake depends on the plant’s health and metabolic rate. This is an important distinction. This is where a metabolism-booster can play a key role. Used together with a balanced fertilization regime, a booster can help to optimize a plant’s performance and allow it grow to its full potential.
Over the last decade, a number of booster-style products have appeared that claim to do just that: speed up the plant’s metabolism and improve its nutrient uptake. But the actual content of these products vary widely, and not every booster is of the same quality. Many don’t even speed up the plants metabolism process but are just phosphorous-type fertilisers that have been named a ‘booster’.
What makes a booster?
So, what makes a good booster product? At CANNA, we believe it is a product, preferably natural, that elicits a response from the plant where the metabolism increases overall and achieves secondary benefits such as:
- a heightened immune response
- faster finishing and
- enhanced quality with no harmful effects to the plant or potential consumer.
Certainly, overloading your plants with phosphorous is not what a good booster product should do. Plant extracts on the other hand, whether crude, dried or fermented, have been shown to influence significantly certain aspects of plant growth, development and even plant health. These plant extracts are the building blocks of true boosters.

How this happens is answered in part by the typical composition of (fermented) plant extracts. Although it does not supply enough nutrients to be a stand-alone fertilizer, it does contain relatively high amounts of micro-nutrients. It is also rich in plant-derived substances like vitamins, carbohydrates and amino acids. All these items come together to enhance the growth and development of a plant at low doses and in a purely natural way. They supplement the fertilization of fruit and vegetable crops when applied through the soil or leaves.
CANNABOOST Accelerator

CANNABOOST Accelerator was launched by CANNA in 2007 after an extensive research project to develop a better plant growth booster than anything available on the market. The resulting product is a liquid metabolism elicitor with high energy content, and with no added plant growth regulators.
Some of the active ingredients of CANNABOOST Accelerator are by-products derived from the production of bio-ethanol and yeast, by fermenting molasses from sugar cane or sugar beet and palm. These by-products are called carbohydrates.
It is important to note that there are many forms of carbohydrates, which is the general term for sugars. It means simply that it is a hydrate of carbon (i.e. carbon with a water molecule attached).
Forms of sugar
There are many forms of sugar. The basic molecule is a single saccharide (monosaccharide). Basic monosaccharides include glucose and fructose. When two monosaccharides join together, they become a disaccharide (sucrose or table sugar). Both monosaccharide and disaccharide carbohydrates are known as sugars and are edible sweet substances.
They are also the basic building blocks for the structure of plant cells and serve as an energy source for processes inside the cell. These saccharides can link together to form a polysaccharide polymer. For example, cellulose is a long-chain structural polymer polysaccharide that is linked together in such a way that it forms permanent bonds that make it a durable molecule. Starch is made up of the same molecules linked in a different way to form a long-chain storage polymer that can be easily broken down.
When a limited number of these saccharides join together – usually between three and ten – and linked to other molecules such as amino acids and proteins, they form polymers known as oligosaccharides (meaning “a few”). They are not sugars but carbohydrates based polymers. These can serve as ways in which cells recognize each other. A simple example is humans blood groups, where oligosaccharides take A, B, or O forms in the walls of the blood cells.
CANNABOOST: a special mixture of saccharides

In CANNABOOST, the oligosaccharide polymer is one of the important elements, with the specific group of oligosaccharides of interest coming from the breakdown of the plant cell as well as the fermentation of micro-organic cells into carbohydrates of a specific length and form.
This is achieved through a very long fermentation process where the plant is first transformed into a thick substance with a high saccharide content. This is known as a molasses soluble and it also contains many other components including vitamins, proteins, amino acids, and many minerals.
Then the fermentation process begins that reduces these simple sugars into ethanol. This ethanol is removed and the remaining components are converted into what becomes CANNABOOST: a specific mixture of oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, amino acids, proteins, other polymers, and other compounds.
The production process is a very long one that involves many steps and just the right types of micro-organisms to produce a product that is of consistently high quality every time. In short, producing CANNABOOST is neither easy nor inexpensive.
How does CANNABOOST work?
The oligosaccharin products that make up CANNABOOST act as triggers in the plant cells. They trigger heightened metabolic processes and have been shown to increase activities including energy production, photosynthesis, metabolite production, gene activation, and so on. The remaining components in CANNABOOST serve to enhance and support these activities, by providing certain levels of important nutrients for example. At the end, no oligosaccharin is left. It is all converted into many components through modern organic chemical techniques that are completely natural. These, together with the trace elements and other remaining components which CANNABOOST contains, directly interact with the metabolic processes in the plant’s cells. CANNABOOST is an all-natural carbohydrate-based product, but it contains little sugar and no added plant hormones at all.
Applying CANNABOOST

foliar spray for a more immediate effect
CANNABOOST can be used as a supplement when feeding your plants. When used in combination with any of the CANNA line of liquid fertilisers, the product has a positive effect on root growth and plant development. The oligosaccharides in CANNABOOST give the plant’s root cells an extra energy shot, allowing the rapid uptake of the minerals available to them. In turn, this improved mineral uptake helps stimulate flowering and increases the quality of taste and smell. Taste and smell is usually based on the mix of sugars, acids and minerals contained within the fruit, and the metabolites they form. CANNABOOST will also elicit a strong response in the plant’s immune reactions, photosynthate production, and metabolic rate.
Alternatively, CANNABOOST can be used as a foliar spray that is applied to the leaves for an immediate boost of photosynthesis. Due to the amount, type, and source of oligosaccharides in the product, the plant cells in the leaves create additional energy that remains available to produce sugars and carbohydrates. These are then available to provide more abundant flowers and better quality fruit. Although foliar spraying can trigger a more immediate boost, the total amount of product needed to obtain the same result as feeding through the root system is higher.
Recommended dosage
The recommended concentration of the CANNABOOST can vary; for a soil or hydroponic application, a dilution of 20 to 40 ml BOOST in 10 litres of water (8-16 ml/ Gal) should be used since the product becomes dispersed in the soil or plant medium and will take longer to reach the active root area.
For a foliar application, a dilution of 20 ml BOOST in 10 litres of water (8 ml/Gal) is sufficient. A leaf application can be viewed as having a more immediate effect, but the grower will have to use it more frequently to get the same result as a soil or hydroponic application to the root system.
In general, a 20 to 40 ml range will give the optimum results. A further increase in the dosage will flatten out the additional growth levels and very high doses may even harm the plant’s development. It will always be up to the individual grower to determine what dosage works best for their particular crop.
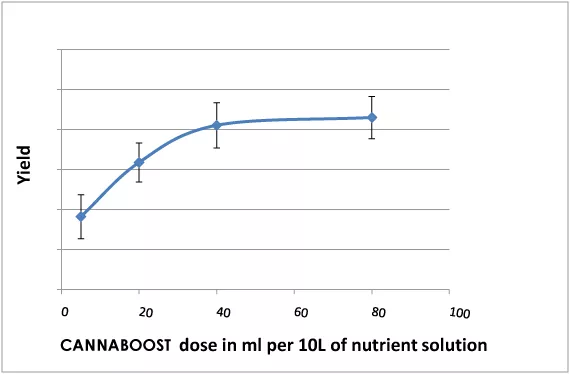
A real boost
CANNABOOST has been specifically developed to give the best results in combination with an optimal fertilizer regime - with CANNA nutrients for flowering plants, for example. CANNABOOST should also be used with PK 13/14, as it supplies the extra levels of phosphorous and potassium that a plant needs for optimal flower / fruit development over a limited and defined period of time. PK 13/14 should still be used when the first flowers appear, in line with current feed schedules.
In general, it is not at all wise to mix fertilizer brands. CANNA fertilisers contain all the necessary nutrients a plant needs for optimal growth when used according to the feed schedules. Other liquid fertilisers may have a destabilizing effect on the substrate and will not necessarily contain the optimum ratio of nutrients.